Blog
Expensive micro organism in moms and newborns can have an effect on the danger of infants for early respiratory infections
In an article just lately printed within the journal Kids’s analysisResearchers examined in Finland whether or not Intestinal microbiota The composition amongst moms and younger infants is related to the danger of creating a respiratory an infection (RTI) in the primary six months of the baby’s life.
They discovered that infants with RTIs had variations within the relative frequency of particular bacterial taxa in comparison with these with out, whereas the complete number of alpha and beta remained comparable. Microbial communities in moms additionally confirmed variations.
background
RTIs are frequent in infancy. Wholesome, full infants in international locations with excessive incomes maintain four to 10 episodes in the primary 12 months. These infections have an effect on the nicely -being of the infants and maintain social and financial penalties. They’ll enhance parental stress and trigger a scarcity of labor.
Curiosity is rising in how early Darmenkrobiota might affect the susceptibility to RTI. Animal research point out that the immunity of the airways is formed by intestinal microbes. Nonetheless, the data of the human research stays inconsistent.
Some analysis work combines low microbial variety and lowered advantageous intestinal micro organism with a increased threat of gasping and bronchial asthma in childhood. Necessary micro organism embrace BifidobacteriumCurrent FacalibacteriumCurrent RuminococcusAnd Roseburia.
Nonetheless, there may be a lot much less nicely identified about direct associations between intestinal microbiota and RTIs in toddler age, particularly as a result of longitudinal research with standardized an infection monitoring and stool samples are restricted in adolescence.
Most earlier research maintain targeted on later outcomes resembling bronchial asthma and never on acute RTIs in adolescence. As well as, maternal microbiota that may have an effect on the toddler rectile Microbiomawas hardly ever examined.
Concerning the research
The researchers establish the speculation that early intestinal microbiota for youngsters along with maternal microbiota might be related to the looks of RTIs in the primary six months of life. They used a nested case management evaluation that included wholesome full -time -finish Finnish infants with start weights of no less than 2.5 kg.
RTI circumstances had been outlined as infants who developed higher RTI with fever, center ear irritation or decrease RTI in the primary six months of life. In the primary four months, the households recorded in a web based diary in the primary four months and two -week medical visits in a web based diary and allow RTI’s exact persecution.
Faecal samples had been collected by moms round their due date and infants aged three and 6 weeks. The rehearsals had been frozen instantly at house and later processed for DNA extraction and the 16S -RRNA gene sequencing to characterize the microbiota composition.
Of 1052 infants within the Helsinki cohort, 189 RTIs developed inside six months. Microbiota information stood for 178 infants and 136 moms within the RTI group as nicely as for 143 infants and 125 moms within the management group with a whole of 461 child and 261 mom samples.
Analyzes in contrast the microbial variety (alpha and beta) and the relative frequency of bacterial staxa between teams. The sensitivity analyzes excluded infections with infections towards stool samples and corresponding circumstances and controls by related elements (start season, gender and supply mode).
Key outcomes
Amongst 178 infants who developed an RTI inside the first six months and 143 management individuals, the center RTI interval was 11 days. Most circumstances had been higher RTIs with fever (49%) or otitis media (47%), whereas solely 4%had been decrease RTIs.
About 30% of the RTI circumstances occurred inside the first three months, most steadily in the center ear otitis. Over half of of the affected infants visited a health care provider and 14% had to wish emergency care, whereas far fewer management individuals had medical visits.
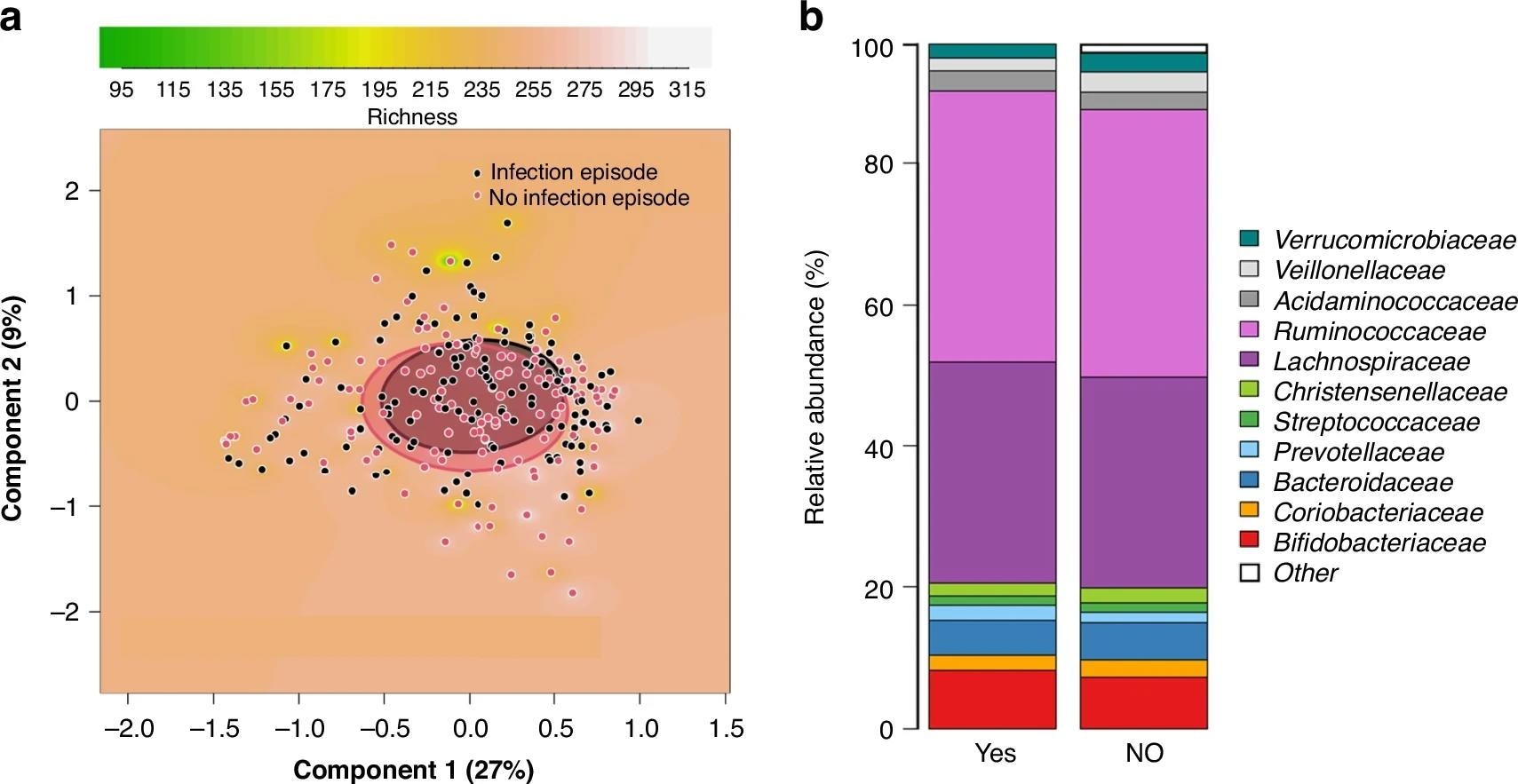
In maternal microbiota, the overall selection and wealth attain not differ between the teams, however moms of infants with RTI had a increased frequency of increased CitrobacterCurrent EnterobacterAnd Enterococcuswhereas Clostridium was decrease. The authors described these micro organism as opportunistic pathogens, which signifies that maternal microbial instability might play a position within the design of the toddler threat.
In infants, the overall composition of the microbial composition was comparable between the teams after 3 and 6 weeks. After three weeks, those that later developed RTIs confirmed AlistipesCurrent AkkermansiaCurrent FacalibacteriumCurrent PeptoniphilusAnd Serratia. The increased wealth of Facalibacterium It was outstanding as a result of earlier research usually related decrease mirrors of this genus with respiratory issues, which highlighted a potential contradiction to earlier outcomes.
After six weeks, Prevotellaceae remained elevated in infants that developed RTIs inside three months, whereas they had been lowered AnaerostipesOne other Butyrat producer was noticed. Anaerostipes Dealing can change the lactate and Butyrat metabolism with potential down -to -date results on immune operate.
Sensitivity analyzes confirmed these outcomes and confirmed constant associations with increased frequencies of Butyrat-producing genera (PseudobutyrivibrioCurrent FacalibacteriumAnd Roseburia), And Proteusand decrease Violet And Anaerostipes For infants that developed RTIs.
Conclusions
In abstract, it might probably be mentioned that the composition of the maternal and early intestinal microbiota -microbiota -mikrobiota composition influences the early susceptibility to RTIs and emphasizes potential targets for preventive interventions in future research. The authors emphasised that these are associations, not the proof of causality, and that the evaluation with an FDR threshold (fake discovery fee) of 0.1 was exploratory. They additional recommended that the early look of butyrat producers of the kind grownup resembling Facalibacterium And RoseburiaMight symbolize an “untimely intestinal microbiota tires” that predisposes infections for an infection.
The strengths of this evaluation embrace the massive cohort for longitudinal strings, systematic parental reporting on delicate RTIs and the evaluation of each toddler and maternal samples. Nonetheless, restrictions have an effect on the comparatively homogeneous inhabitants with excessive incomes, common breastfeeding and a restriction for wholesome, full infants that restrict generalizability.
be aware
Some microbial associations (e.g. with FacalibacteriumCurrent RoseburiaAnd Pseudobutyrivibrio) had been most evident in sensitivity analyzes that excluded infants with early infections and matched the controls attributable to perinatal elements. These had been not all the time in essentially the most critical unsurpassed evaluation. Readers ought to interpret these outcomes as exploratory associations fairly than a constant causal indicators.
Journal Reference:
- The affiliation of moms and hanging early intestinal microbio with respiratory topics. Hyvönen, S., Saarikivi, A., Mälkönen, J., Solasaari, T., Korpela, Okay., de Vos, WM, Salonen, A., Ruuska-Loewald, T., Kolho, Okay. Kids’s analysis (2025). Two: 10.1038/S41390-025-04326-0 ,, https://www.nature.com/articles/s41390-025-04326-0